You’re on the brink of a significant milestone — retirement. The “Retirement For Social Security” article is tailored just for you. It’s a comprehensive guide designed to help you navigate the Social Security system, unveiling all its nooks and crannies. From maximizing benefits to understanding its intricacies, this will be your compass guiding you through making informed decisions that will shape the quality of your golden years. You are not just retiring, but you’re stepping into a future strengthened by an understanding of the Social Security system.
This image is property of assets-global.website-files.com.
Check out our recommended retirement gifts!
- Understanding the Role of Social Security in Retirement
- Planning for Retirement – The Social Security Aspect
- Eligibility for Social Security Benefits
- Claiming Social Security Before Full Retirement Age
- Deferring Social Security Benefits
- Managing Social Security Benefits in Retirement
- Effect of Continued Employment on Social Security Benefits
- Survivor Benefits and Social Security
- Considering Social Security Disability Benefits
- Addressing Concerns about Social Security Fund’s Future
Understanding the Role of Social Security in Retirement
Social security represents an integral part of your retirement plan. Around nine out of ten individuals aged 65 and above receive social security benefits, making it a key source of retirement income for most Americans.
Overview of Social Security benefits
Social Security benefits are a type of government-backed retirement income. They are a major income source for many retirees, as they are intended to substitute a portion of your income based on your lifetime earnings. The benefits you receive are calculated based on your highest 35 years of earnings and your age at which you choose to start getting benefits.
Importance of Social Security for retirees
Social Security benefits are crucial for retirees as they provide a steady source of income that they can count on. Beyond merely replacing a portion of your income upon retirement, social security also offers benefits to your dependents and survivors in case of your demise, hence its significance in providing financial safety for your loved ones.
How Social Security payments are calculated
The amount of Social Security benefits one receives is calculated according to their lifetime earnings. The Social Security Administration utilizes a complex formula that considers your 35 highest-earning years. The monthly payments may increase or decrease depending on the age when you start claiming the benefits.
Planning for Retirement – The Social Security Aspect
Planning your retirement financially includes understanding how much you might receive from Social Security and decoding the perfect time to start these benefits.
Assessing your future Social Security benefits
You can estimate your future Social Security benefits by utilizing online tools provided by Social Security Administration, or by viewing your Social Security statement. It’s also important to note your earnings record because any inaccuracies can potentially impact the benefits you’re entitled to.
Incorporating Social Security benefits into retirement planning
Social Security Benefits shouldn’t be viewed as your only source of income at retirement. They should form part of your wider retirement investing strategy, supplementing retirement savings that ensure lifestyle sustainability throughout your golden years.
Understanding the right time to claim Social Security benefits
Understanding when to claim Social Security benefits is vital. If you claim before your full retirement age, your benefits get reduced, but you receive them over a longer period. On the other hand, if you wait until after full retirement age, your benefits increase, but you’ll receive them over a shorter period. The decision truly depends on your specific circumstances.
Check out our recommended retirement gifts!
Eligibility for Social Security Benefits
To receive Social Security benefits, certain criteria must be fulfilled. These norms vary depending on the type of benefits.
Age requirements for Social Security benefits
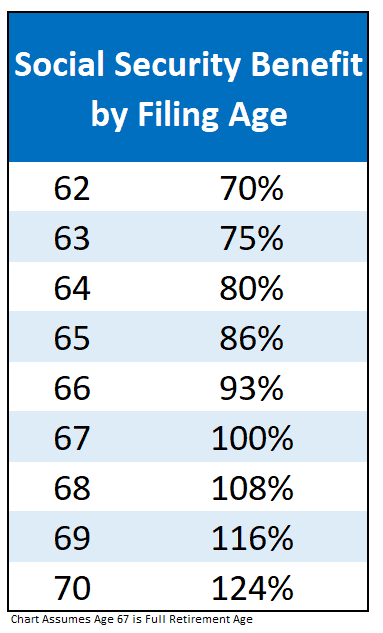
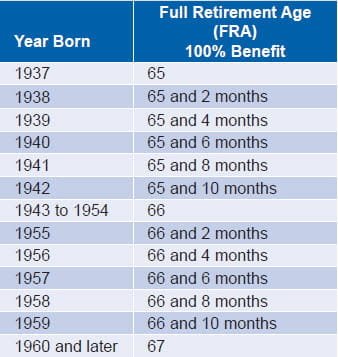
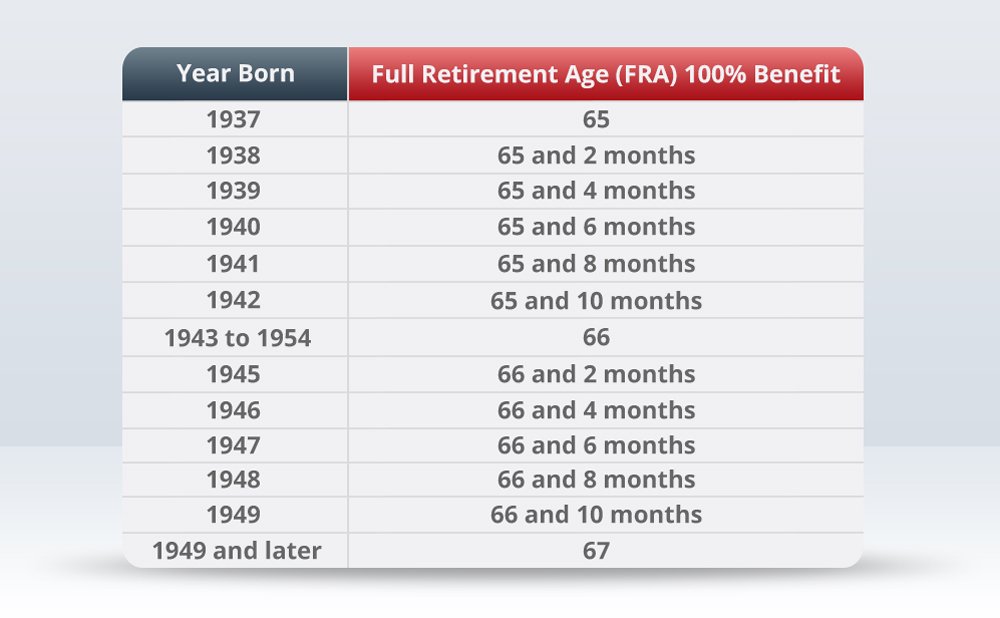
The full retirement age varies depending on your birth year. However, you can start receiving benefits from age 62, at a reduced rate. Waiting until full retirement age or beyond can result in larger benefit checks.
Impact of employment history on eligibility
You need to earn a certain number of credits to be eligible for Social Security retirement benefits. These are earned through income earned from work. The amount of income needed for a credit increases each year.
Addressing potential eligibility issues
It’s important to know what issues may impact your eligibility for Social Security benefits. Examples include incomplete work history, disability, or any other special circumstances. Knowing and addressing these issues will help you plan your retirement efficiently.
Claiming Social Security Before Full Retirement Age
Choosing to claim Social Security benefits before reaching full retirement age has both pros and cons.
Understanding reduction in benefits
If you start receiving benefits early, your benefits may be reduced by a fraction of a percent for each month before your full retirement age.
Evaluating the advantages and disadvantages
While claiming early results in smaller payments, it may be advantageous if you need the income immediately or if you have health concerns that might limit your lifespan. On the other hand, waiting until full retirement age allows for larger monthly payments.
Impact on spousal benefits
The decision to take early retirement also impacts spousal benefits. If you take your benefits early, the spousal benefits will also be reduced.

This image is property of www.planmember.com.
Deferring Social Security Benefits
You can also choose to defer Social Security benefits past your full retirement age.
Benefits of delaying claim
Delaying your Social Security benefits can result in larger monthly payments later. For every year you delay past your full retirement age, your retirement benefits can increase by a certain percentage up until age 70.
How deferring impacts overall retirement funds
Despite the increase in monthly benefits, choosing to delay must be carefully considered concerning overall retirement funds. It involves estimating the breakeven point when the value of higher delayed benefits exceeds the value of receiving lowered benefits early.
Role of longevity and health in deciding to defer
The decision to defer can be guided by factors such as your health status and the length of your expected lifespan based on health history and lifestyle.
Managing Social Security Benefits in Retirement
Managing your Social Security benefits during retirement involves strategies to maximize benefits and mitigate taxes.
Managing benefit payments effectively
It becomes essential to plan for expenses and handle benefit payments wisely to ensure they last across your retirement life.
Role of other income sources in retirement
While Social Security forms a significant part of retirement income for many individuals, it won’t likely be enough. Hence, it’s important to have other income sources, such as savings, investments, and pensions.
Planning for taxes on Social Security benefits
Depending on your overall income, a portion of your Social Security benefits may be taxable. Hence, planning for tax payments is a critical aspect of managing Social Security income during retirement.
This image is property of www.michigan.gov.
Effect of Continued Employment on Social Security Benefits
Working while receiving Social Security benefits can have implications on your benefits and taxes.
Impact of earnings limit
There is an annual limit to how much you can earn while collecting Social Security benefits if you are younger than full retirement age. If you exceed the limit, your benefits may be reduced.
Influence on benefit amount
If you continue to work during retirement, ongoing wages could increase future benefits because Social Security takes into account your highest 35 years of earnings when calculating benefits.
Understand tax obligations
Working while receiving benefits could also increase the amount of your Social Security benefits that are subject to income taxes.
Survivor Benefits and Social Security
Social Security provides benefits to surviving spouses and children.
Understanding survivor benefits
Survivor benefits are intended to provide financial support to your family after your demise. A surviving spouse, former spouse, children under 18 (or older if disabled before turning 22), and even parents in some cases, may be eligible.
Claiming options for widows and widowers
Widows and widowers can begin claiming survivor benefits as early as age 60, albeit at a reduced rate. They are eligible for full benefits at their full retirement age.
Impact of remarriage on survivor benefits
Remarrying before reaching age 60 could affect eligibility for survivor benefits. However, remarriage after age 60 doesn’t impact one’s ability to claim survivor benefits on a previous spouse’s record.
This image is property of www.londoneligibility.com.
Considering Social Security Disability Benefits
Disability can alter one’s plans significantly. Understanding Social Security disability benefits can help cope with such situations.
Eligibility and assessment for disability benefits
To be eligible for disability benefits, one must meet the Social Security Administration’s definition of disability. The severity of the disability and the likelihood of it lasting for at least a year or resulting in death are taken into consideration.
Role of disability benefits in retirement planning
Inclusion of disability benefits in retirement planning prepares one for contingencies. In the event of disability, these benefits may replace a portion of your income.
Transition from disability to retirement benefits
Benefits automatically convert from disability to retirement benefits once you reach full retirement age with no reduction in amount.
Addressing Concerns about Social Security Fund’s Future
Will the Social Security system exist when you retire? This concern often clouds retirement planning.
Understanding the financial status of Social Security program
The Social Security program is predominantly funded through payroll taxes. The fund’s trustees report provides an insight into its financial status.
Potential impacts on future retirees
Though the trust funds are expected to deplete in the coming years, incoming payroll taxes could still cover approximately three-quarters of scheduled benefits.
Measures taken to secure the future of Social Security
Several proposals aimed at preserving the Social Security system are being considered. They range from increasing the payroll tax rate to raising the ceiling on taxable wages.



