Imagine working hard all your life, looking forward to retirement, and suddenly being hit with the unexpected: taxes on your retirement benefits? It’s a scenario you would rather avoid, right? In “Are Retirement Benefits Taxable”, we explore this important personal financial matter. This article explores the realities of taxes on retirement benefits, offering a balanced view to help you better understand this often complex area of financial planning. It aims to reduce uncertainty while preparing you for retirement, ensuring you can enjoy your golden years without unwelcome surprises.

Check out our recommended retirement gifts!
- Understanding Retirement Benefits
- Taxation Basics
- How Retirement Benefits Are Taxed
- Social Security Benefits and Tax
- Pension Plans and Tax
- Retirement Account Rollovers and Tax
- Annuities and Tax
- Life Insurance and Retirement Benefits Tax
- Understanding the Retirement Savers Credit
- Retirement Tax Planning Strategies
Understanding Retirement Benefits
Retirement benefits refer to the income sources that you can rely upon once you make the shift away from full-time employment. Typically, such benefits are designed to replace your regular paychecks and help you maintain the lifestyle you’re accustomed to, even when you are no longer working.
What Are Retirement Benefits
In a nutshell, retirement benefits are the various payouts you receive post-retirement to ensure financial security during your golden years. They can come from different sources such as government-sponsored Social Security, employer-sponsored pension plans, and your personal retirement savings or investments like Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) and 401(k)s.
Different Types of Retirement Benefits
The different types of retirement benefits are diverse and include Social Security, pensions, retirement plans (like 401(k) and IRAs) profit-sharing, stock bonus plans, and even life insurance annuities. Each comes with its own set of rules regarding contribution, accrual, distribution, and taxation, underscoring the importance of understanding each component in detail.
Taxation Basics
Before getting into the nitty-gritty of how retirement benefits are taxed, it’s useful to brush up on some tax basics first.
What is Taxable
Most types of income are taxable. This includes wages, salary, tips, bonuses and other forms of compensation for services rendered. It also includes income from investments like interest, dividends, rent, and gains from the sale of investment assets.
What Is Not Taxable
There are also forms of income that are generally not taxable. These might include gifts and inheritances, child support payments, welfare benefits, and cash rebates from a dealer or manufacturer for an item you buy.
Basic Tax Terminology
Words like gross income, adjusted gross income (AGI), tax deductions, tax credits, tax bracket, and taxable income are important to understand when dealing with taxes. Gross income is your total income from all sources. Adjusted gross income is gross income minus certain adjustments. Taxable income is what’s left after all deductions and exemptions. A tax bracket is the tax rate applied to your taxable income.
Check out our recommended retirement gifts!
How Retirement Benefits Are Taxed
Just like your regular income, your retirement income can also be subject to taxes, although the specific rules can vary depending on the type of benefit and how much you receive.
Taxation on Retirement Account Withdrawals
Generally, withdrawals from a traditional IRA or 401(k) plan are taxed as ordinary income. If you’ve made non-deductible contributions, a portion of the distribution is tax-free, while the remainder is taxable.
Roth IRAs and Tax-free Withdrawals
Contrary to traditional IRAs and 401(k)s, Roth accounts are funded with after-tax dollars, meaning that withdrawals in retirement are generally tax-free provided certain conditions are met.
Required Minimum Distributions and Tax
Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) refer to the minimum amount you must withdraw from your retirement account each year after you reach a certain age (currently 72 for most account holders). These distributions are usually subject to regular income tax.
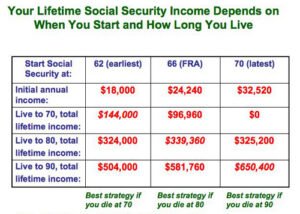
Social Security Benefits and Tax
Your Social Security benefits can be taxable depending on your overall income level.
How Social Security Benefits Are Taxed
The taxation of your Social Security benefits depends on your “combined income,” which includes your adjusted gross income, tax-exempt interest, and half of your Social Security benefits. Depending on this, up to 85% of your benefits may be taxable.
Factors Influencing Tax on Social Security Benefits
Several factors – including your filing status, total income, and state of residence – can affect how much of your Social Security is taxable.

Pension Plans and Tax
Conventional pension plans, also known as defined benefit plans, are also subject to taxes, which depend on various factors.
Taxability of Pension Plan Benefits
The portion of your pension that’s funded by pre-tax contributions will generally be taxable as income once distributed to you. However, if you made after-tax contributions to your pension, a part of each payout is a tax-free return of these contributions.
How Lump-sum Distributions Are Taxed
If you choose to receive your pension as a lump sum, this distribution may be subject to income taxes in the year you receive it.
Retirement Account Rollovers and Tax
Without careful planning, rolling over retirement savings from one account to another can create a taxable event.
What Are Rollovers
A rollover occurs when you move funds from one retirement savings plan to another. This might happen if you change jobs or retire and need to move your accumulated savings into a different account.
How Rollovers Are Taxed
Generally speaking, rollovers are not taxed provided the funds are deposited in the new retirement account within 60 days.
Annuities and Tax
Annuities can be a consistent source of retirement income. They’re often funded with pre-tax dollars and thus have important tax implications.
What Are Annuities
Annuities are contracts you purchase from an insurance company to pay you income at later dates. Payments may occur for a fixed number of years or for your lifetime.
How Annuities Are Taxed
The taxation of annuities depends on whether they were purchased with pre-tax or after-tax dollars, affecting whether withdrawals will be fully taxable or partially taxable.
Life Insurance and Retirement Benefits Tax
Life insurance can serve as both an income replacement tool and a source of potential retirement income.
Life Insurance as a Retirement Benefit
Certain life insurance policies allow for tax-deferred growth of cash value, which you can access during retirement as supplemental income via loans or withdrawals.
How Life Insurance Benefits Are Taxed
The death benefit of a life insurance policy is typically tax-free for the beneficiary. However, loans or withdrawals from the cash value of a policy are often taxable.
Understanding the Retirement Savers Credit
The Retirement Savers Credit is a tax credit available to eligible taxpayers who save for retirement.
Eligibility for the Retirement Savers Credit
To qualify for this credit, there are several requirements regarding age, filing status, and income.
How the Retirement Savers Credit Affects Taxes
This tax credit can reduce your federal income tax on a dollar-for-dollar basis, thereby incentivizing retirement saving.
Retirement Tax Planning Strategies
Proper tax planning in retirement can save you thousands of dollars.
Importance of Tax Planning in Retirement
Effective tax planning can help minimize your tax bill, preserve more of your accumulated wealth, and provide more money for you to spend or leave to loved ones.
Ways to Minimize Tax on Retirement Benefits
Several strategies can help reduce your tax bill in retirement, such as understanding when to start taking Social Security, strategically planning your retirement account withdrawals, and deciding between Roth and Traditional retirement accounts.